Introduction to Nail Psoriasis vs. Fungus
Nail psoriasis and fungal infections are two common conditions that affect the nails. While they may share some similar symptoms, it is crucial to distinguish between the two for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
In this article, we will provide a brief overview of nail psoriasis and fungal infections, highlighting the importance of recognizing the differences between these conditions.
Understanding Nail Psoriasis
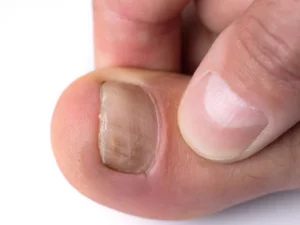
A. Definition and Causes of Nail Psoriasis
Nail psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the skin and nails.
It occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells, leading to inflammation and an accelerated turnover of skin cells.
The exact cause of nail psoriasis is not fully understood, but genetic factors, environmental triggers, and an overactive immune system are believed to contribute to its bdevelopment.
B. Symptoms and Appearance of Psoriasis Nails
Psoriasis nails often exhibit specific characteristics that differentiate them from fungal infections.
Common symptoms include pitting (small depressions), ridges, discoloration, thickening, crumbling, and separation of the nail from the nail bed. Psoriasis nails may have a “sandpaper-like” texture or appear dull and rough.
These visual cues can be helpful in distinguishing nail psoriasis from other conditions, such as fungal infections.
C. Risk Factors and Common Triggers for Nail Psoriasis
Several risk factors and triggers can contribute to the development or exacerbation of nail psoriasis.
These include a family history of psoriasis, previous skin or nail trauma, infections, hormonal changes, certain medications (such as beta-blockers or lithium), stress, smoking, and obesity.
Identifying and addressing these risk factors can help manage the condition effectively.
D. Impact on Overall Health and Potential Complications
Nail psoriasis can have a significant impact on an individual’s quality of life and overall health. Besides the discomfort and pain that can arise from nail changes, it can also cause emotional distress and affect self-esteem.
Nail psoriasis is often associated with other forms of psoriasis, such as plaque psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis.
Additionally, severe cases of nail psoriasis can lead to functional impairment, making it difficult to perform daily activities. In some instances, nail psoriasis may result in secondary infections or nail deformities.
Recognizing Nail Fungus (Onychomycosis)
A. Definition and Common Causes of Nail Fungus
Onychomycosis, commonly referred to as nail fungus, is a fungal infection that specifically targets the nails. It is usually caused by various types of fungi, including dermatophytes, yeasts, and molds.
Fungal spores can enter the nail through small cracks or cuts, leading to an infection.
B. Symptoms and Appearance of Fungal Nail Infections
Fungal nail infections often present with distinct symptoms and appearance. Affected nails may become thickened, brittle, and discolored, often displaying a yellowish or brownish tint. As
the infection progresses, the nails can become distorted in shape, crumbly, or separated from the nail bed. These symptoms are different from the characteristic features of nail psoriasis.
C. Risk Factors and Factors That Increase the Likelihood of Fungal Nail Infections
Several risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing fungal nail infections.
These include frequent exposure to warm and humid environments, wearing tight or non-breathable footwear, poor foot hygiene, compromised immune system, pre-existing nail conditions (such as nail trauma or psoriasis), and certain medical conditions like diabetes.
Gaining an understanding of these risk factors help individuals to proactively implement preventive measures.
D. Potential Complications and Associated Health Concerns
If left untreated, fungal nail infections can lead to various complications. The infection can spread to other nails or even the surrounding skin, causing athlete’s foot or cellulitis.
In individuals with compromised immune systems or underlying medical conditions, fungal nail infections may pose a greater risk. Furthermore, severe cases of fungal nail infections can result in permanent nail damage or complete loss of the nail.
Differentiating Nail Psoriasis from Fungal Infections
A. Key Differences in Symptoms and Appearance
Nail Psoriasis: Nail psoriasis is characterized by nail discoloration, pitting (small depressions), crumbling, thickening, and other irregularities. The nails may also show signs of separation from the nail bed. These symptoms are distinct from those of fungal infections.
Fungal Infections: Fungal nail infections typically cause thickened, brittle nails with a yellowish or brownish color. The nails may become distorted in shape and crumble easily. Unlike nail psoriasis, fungal infections do not typically cause pitting.
B. Diagnostic Methods and Tests
To accurately diagnose nail psoriasis or a fungal infection, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional or dermatologist. They may conduct a physical examination, review medical history, and perform tests such as a nail sample analysis or a skin biopsy.
These diagnostic methods help identify the underlying cause and differentiate between nail psoriasis and fungal infections.
C. Consulting a Healthcare Professional
Given the similarities in symptoms, it is important to seek professional medical advice for an accurate diagnosis. A healthcare professional can differentiate between nail psoriasis and fungal infections based on their expertise and the results of diagnostic tests. They can then recommend proper treatment options.
Treatment Options for Nail Psoriasis and Fungal Infections
A. Treatment Approaches for Nail Psoriasis
Topical Treatments: Corticosteroids or vitamin D analogs may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and promote healthy nail growth.
Phototherapy: Exposure to ultraviolet light may help improve nail psoriasis symptoms.
Systemic Medications: In severe cases, systemic medications like methotrexate or biologics may be prescribed to suppress the immune response and manage nail psoriasis.
B. Treatment Options for Fungal Nail Infections
1. Antifungal Medications: Oral or topical antifungal medications are commonly prescribed to eradicate the fungal infection.
2. Topical Creams: Antifungal creams or ointments may be used to treat superficial fungal infections.
3. Nail Removal: In severe cases or when other treatments fail, surgical options such as nail removal may be considered.
C. Lifestyle Changes and Self-Care Tips
In addition to medical treatment, there are self-care tips and lifestyle changes that can help manage both nail psoriasis and fungal infections.
These include keeping nails trimmed and clean, avoiding trauma to the nails, wearing breathable footwear, practicing good hand and foot hygiene, and using antifungal powders or creams as recommended.
Prevention and Long-term Management
A. Preventive Measures
To reduce the risk of nail psoriasis and fungal infections, it is important to take preventive measures.
These include avoiding triggers such as stress and infections for nail psoriasis and practicing good foot hygiene to prevent fungal infections. Wearing clean socks and breathable shoes and avoiding walking barefoot in public areas can also help prevent fungal infections.
B. Strategies for Maintaining Healthy Nails
Maintaining overall good health, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management, may contribute to better control of nail psoriasis symptoms.
For fungal infections, keeping nails dry and trimmed, avoiding non-breathable footwear, and using antifungal products when necessary are important.
C. Regular Monitoring and Follow-ups
Regular monitoring and follow-ups with a healthcare professional are crucial for both conditions. They can assess treatment progress, provide additional recommendations, and adjust the treatment plan if needed. Regular check-ups help manage the conditions effectively and prevent complications.
Conclusion
Distinguishing between nail psoriasis and fungal infections is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
Understanding the key differences in symptoms, appearance, and diagnostic methods can help individuals seek appropriate medical care.
With the right diagnosis, treatment options tailored to each condition can be pursued, and lifestyle changes can be implemented to manage and prevent nail psoriasis and fungal infections effectively.
If you suspect you have either condition, it is important to consult a healthcare professional or dermatologist for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
Feel free to leave a comment below, and also share this article with anyone whom you think may benefir from it.
